
|
Climate is the long-term weather conditions of an area. Average rainfall, air temperature, humidity, and wind speeds determine an area's climate. The
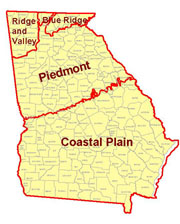
Altamaha River watershed spans the Coastal Plain and Piedmont geological
regions in Georgia (more on Georgia's Geology).
These two geological regions have a humid subtropical climate. This
type of climate has long, hot summers. Winters are short and mild.
Rain may fall at all times of the year. This humid subtropical climate
is caused by several factors: a southern location, low elevation,
and nearness to the warm waters of the Atlantic Ocean and Gulf of
Mexico. In
the Blue Ridge, Valley and Ridge, and Cumberland Plateau regions
to the north, the climate is classified as humid continental. In
these areas, summer temperatures are cooler than in southern Georgia.
Winters are colder, although not severe. Some winter snowfall occurs
in the northern regions. The mountainous Blue Ridge region receives
the most precipitation (rainfall and snowfall) in the state. Moist
air from the ocean rises when it meets the mountains. At these high
elevations, the moist air cools and may fall as rain or snow (more
on the water
cycle). Throughout the state of Georgia, winter and summer are the rainiest seasons. The average yearly precipitation is about 1270 mm (about 50 in). The lowest temperature recorded in the state was -27.2° C (-17° F). This was recorded near Rome in the northwest in 1940. The highest temperature recorded in the state was 44.4° C (112° F). This was recorded in 1952 in Louisville in the east (near (landmark/town). This is not too bad - the lowest temperature ever recorded in an inhabited place is -68° C (-58° F) (recorded in Oymyakon, Siberia). The highest temperature ever recorded is 58° C (136° F) (recorded in Libya in northern Africa). |
 |
||
 |
|||